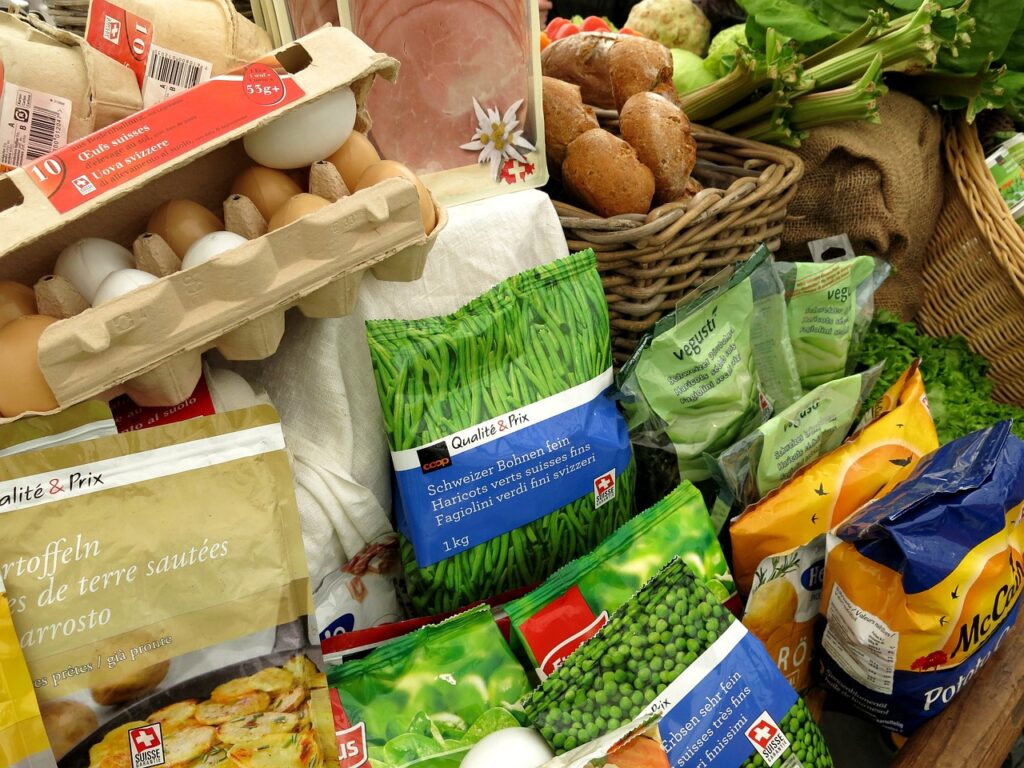
In today’s fast-paced world, packed food holds a significant place. Due to daily commutes and busy schedules, people often don’t have enough time to cook, so they prefer packed foods, whether they are dairy products, vegetables, snacks. Some packed foods are partially cooked, such as frozen vegetables or instant noodles that cook in two minutes. While these options save time and are tasty, they come with both benefits and side effects, which we will explain in this article. So, be sure to read the entire article.
Benefits of Packed Food
- Convenience: The biggest benefit of packed food is how easy it is to prepare. It saves time, which is very helpful for busy people. City folks find this convenience especially useful. People who work long hours often don’t have time to cook, so they go for packed foods that are ready in just a few minutes.
- Long Shelf Life: Compared to fresh food, packed food has a longer shelf life. This means packed food doesn’t spoil as quickly. Various preservation methods are used to extend its life:
- Freezing: Food is kept at very low temperatures, which prevents the growth of bacteria and microorganisms.
- Canning: Food is sealed in cans and heated to high temperatures, killing microorganisms and keeping the food safe for a long time.
- Vacuum Sealing: Air is removed from the packet, reducing the oxygen level and stopping the growth of bacteria.
- Preservatives: Some packed foods contain chemical preservatives that help keep the food fresh for a longer time.
- Dehydration: Food is dried out by removing its water content, which prevents the growth of bacteria and helps the food stay safe for a longer period.
3. Consistency: It ensures the same taste every time. The quality and flavor remain uniform.
4. Hygiene: Special attention is given to hygiene. It is packed in a very clean and safe manner, which reduces the risk of diseases.
5. Accessibility: Packed food is available in various options, catering to different tastes.
6. Nutrition: Packed food often contains specific nutritional elements such as vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which can be beneficial for health.
7. Variety: It offers a range of different foods and snacks, providing diversity in what you can eat.
Limitation of packed food
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Packed food sometimes contains high amounts of salt, sugar, and trans fats, which can be harmful to health and may also lead to nutritional deficiencies.
- Lack of Natural Ingredients: Packed food often contains artificial colors and fflavors, which can lead to a lack of natural nutrients.
- Health Risks: Some packed foods contain high levels of junk food ingredients, which can cause digestive issues . This can increase the risk of obesity, heart disease, and other health problems.
- Environmental Impact: Packed food is often packaged in plastic and other non-biodegradable materials, which can contribute to environmental pollution.
- Taste Variability: Some packed foods can have varying tastes, which may differ significantly from fresh food.
- Costly: Packed food is often more expensive than fresh food, which can impact your budget.
Types of Packed Food
- Canned Food: Food that is packed in metal cans and preserved through heating, which helps keep the food safe and fresh for a long time.
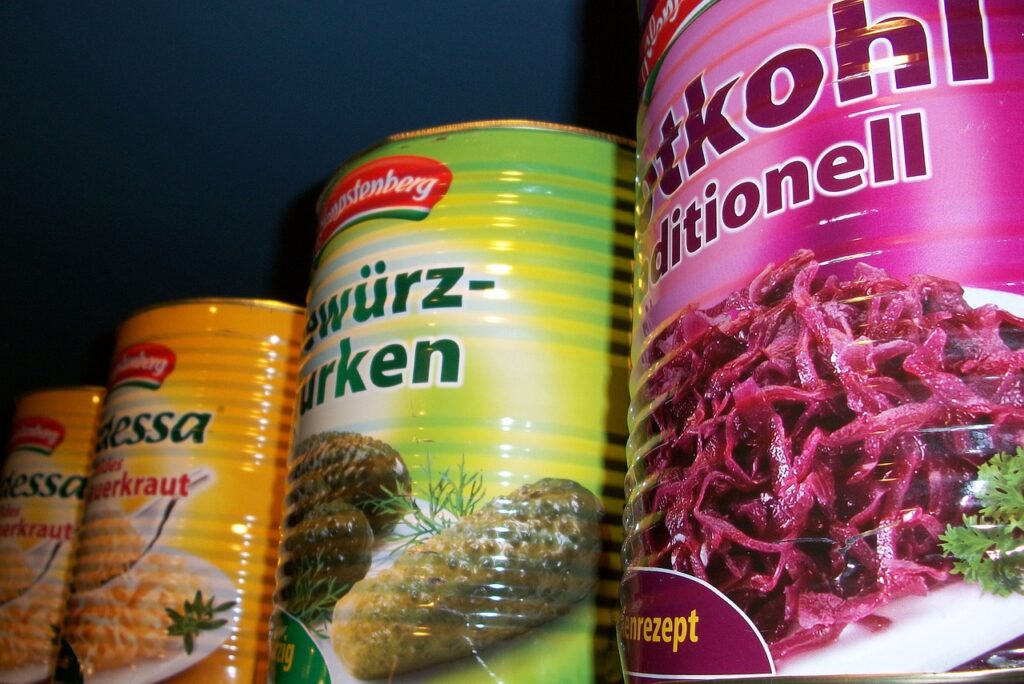

- Fruit Cans: Such as pineapple, apples, and peaches.
- Vegetable Cans: Such as green peas, okra, and corn.
- Meat Cans: Such as beef, chicken, and turkey.
- Soup and Stew Cans: Such as tomato soup and chicken stew.
- Dessert Cans: Such as halwa and pudding packed in cans.
2. Frozen Food: Frozen food refers to food items that are preserved by cooling and freezing. This process helps keep the food fresh and safe for a long time.
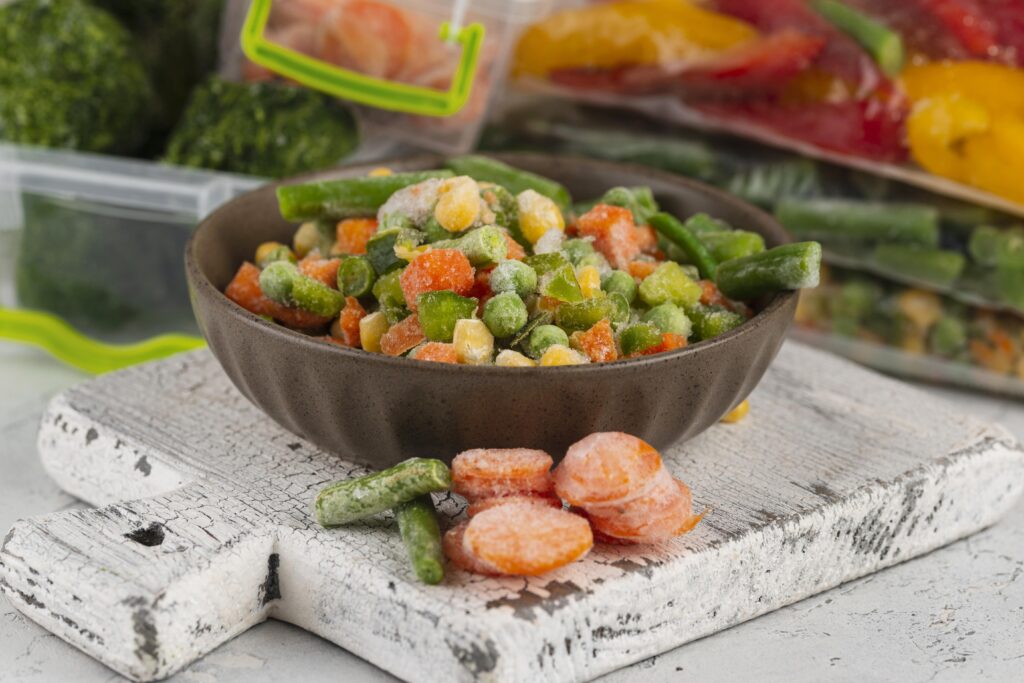

- Fruits: Such as berries, strawberries, and mangoes.
- Vegetables: Such as carrots, green peas, and spinach.
- Meats: Such as chicken, beef, and fish.
- Snacks: Such as frozen pizza and French fries.
- Ready Meals: Such as frozen burgers and soups.
3. Snacks: Snacks are small foods that people eat between main meals or as a light bite. They can be fresh or packaged and are usually quick to prepare.
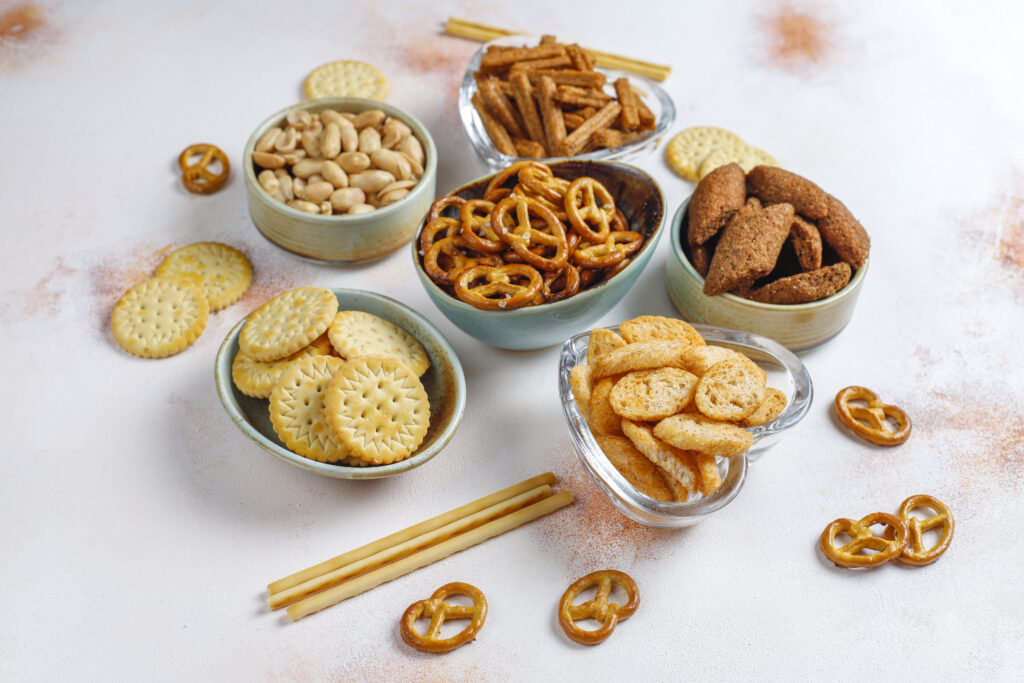

- Nuts and Beans: Like peanuts, almonds, and cashews.
- Biscuits and Cookies: Like shortbread and chocolate chip cookies.
- Dried Fruits: Like raisins, figs, and apricots.
- Chips and Fries: Like potato chips, French fries, and fried snacks.
- Packaged Snacks: Like pre-packaged popcorn, snack bars, and pizza rolls.
Benefits
- Convenience: Snacks are quick and easy to prepare.
- Variety: There are many types of snacks to choose from, depending on taste and preference.
- Energy: Some snacks provide a quick energy boost.
Limitations
- Nutritional Issues: Many snacks have high amounts of sugar, salt, and trans fats.
- Health Risks: Eating too many snacks can lead to weight gain and other health problems.
- Taste Variability: Some packaged snacks may taste less fresh compared to homemade options.
Health Tips
- Balanced Choices: Choose healthier snacks like nuts and dried fruits.
- Moderation: Eat snacks in moderation and not as a replacement for main meals.
Comparisons between Packed food and Fresh food
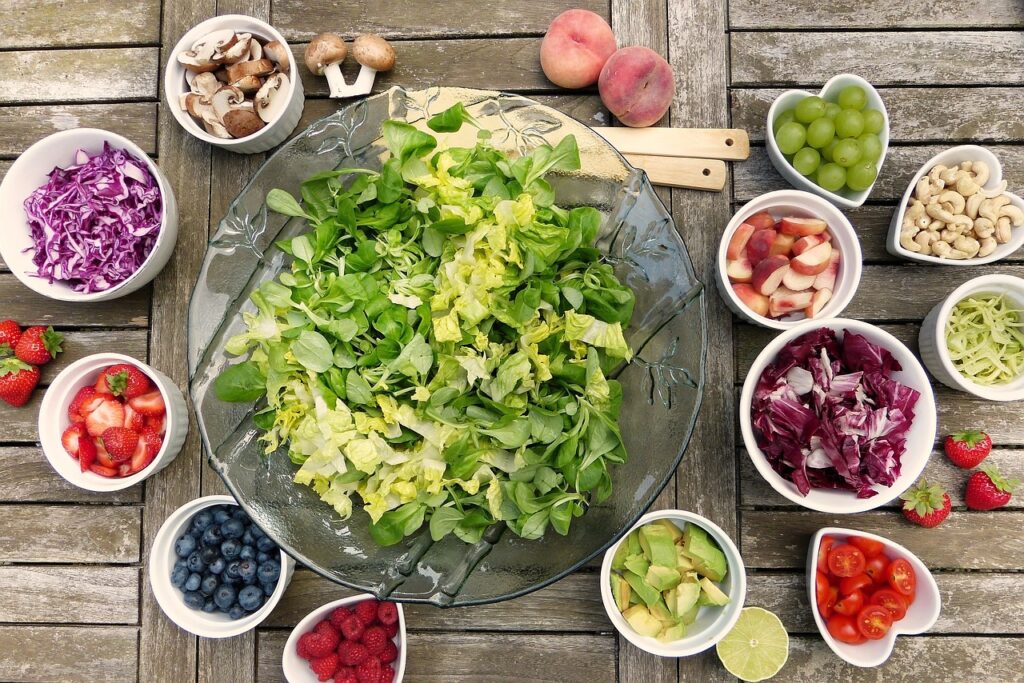

- Packed Food: It may contain higher levels of sugar, salt, and preservatives, which can reduce the nutritional value.
- Fresh Food: It contains vitamins, minerals, and natural nutrients.
- Taste: Packed food might have varying taste and could be less fresh compared to fresh food, which usually has a more natural and better taste.
- Convenience: Packed food can be prepared quickly, whereas fresh food takes more time to prepare.
- Shelf Life: Packed food can be stored for a long time, while fresh food spoils quickly and remains fresh for a limited period.
- Health Impact: Excessive consumption of packed food can negatively affect health, while fresh food is generally better and more balanced for health.
Conclusion:
Packed food and fresh food both have their advantages and limitations. Packed food is convenient but often contains high levels of sugar, salt, and artificial colors and flavors to maintain taste. Chemicals are also used to preserve it, which can negatively impact our health. On the other hand, fresh food has natural taste and color and is rich in vitamins and minerals, which helps meet our nutritional needs. However, fresh food takes more time to prepare and has a shorter shelf life compared to packed food.
For a healthier, medicine-free life, I recommend choosing fresh food. Thank you for reading this article.